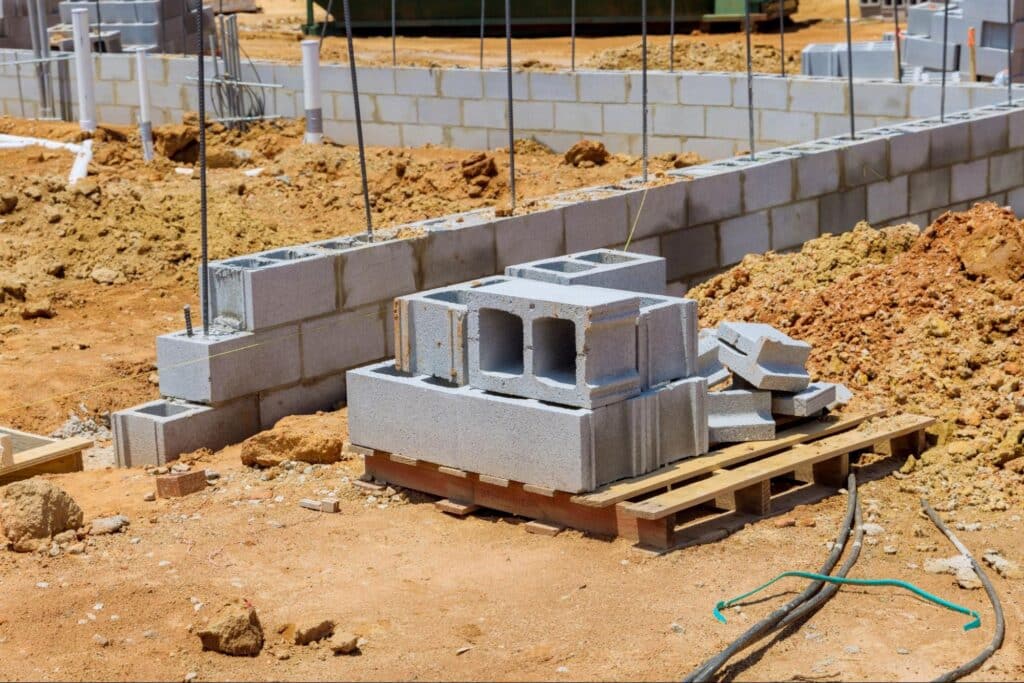
Block foundations are widely used for their solid vertical support and durability when properly reinforced. While their lower material costs can be appealing, the installation is labor-intensive, meaning the true cost and efficiency depend on project-specific factors like site complexity and labor rates. Whether you’re planning to build a new home in Southern Indiana or Eastern Illinois or maintaining an existing one, understanding this balance is key to protecting your investment.
This guide covers everything from construction and maintenance to how a well-built block foundation fits into the quality approach at Reinbrecht Homes.
The Block Foundation: A Balancing Act of Strengths and Considerations
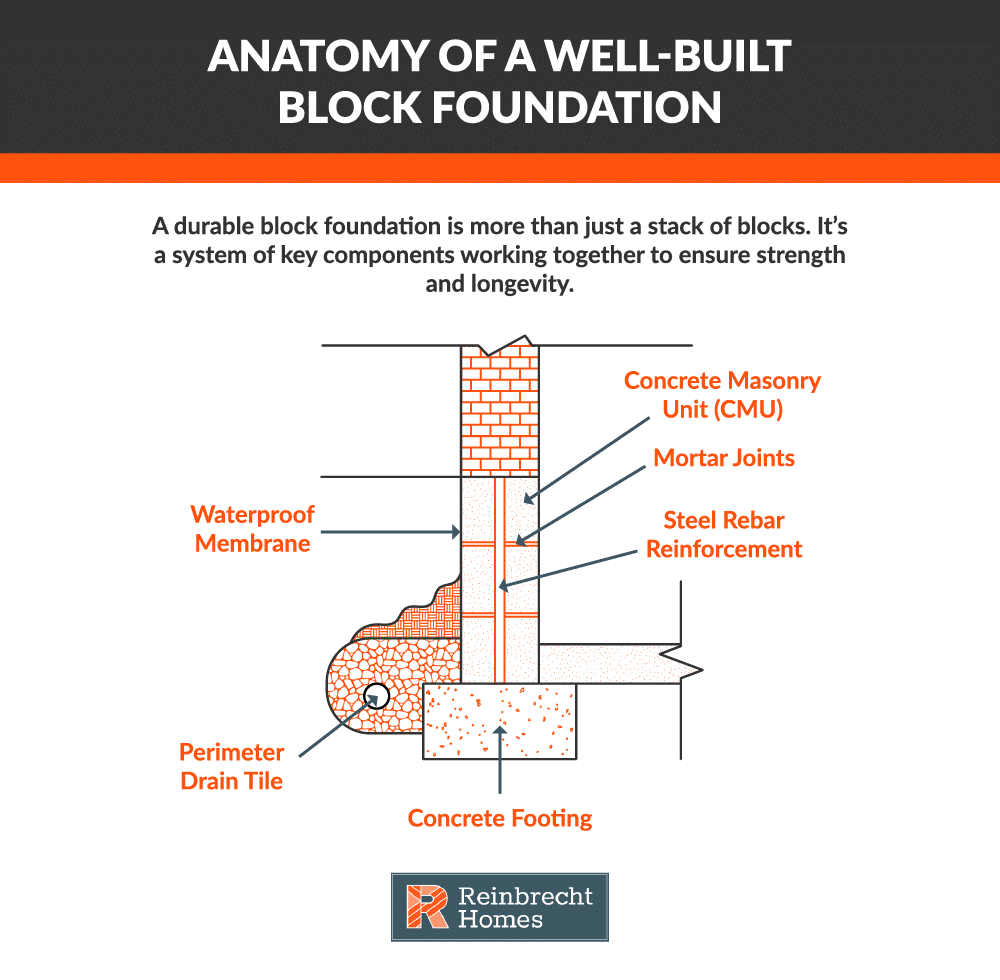
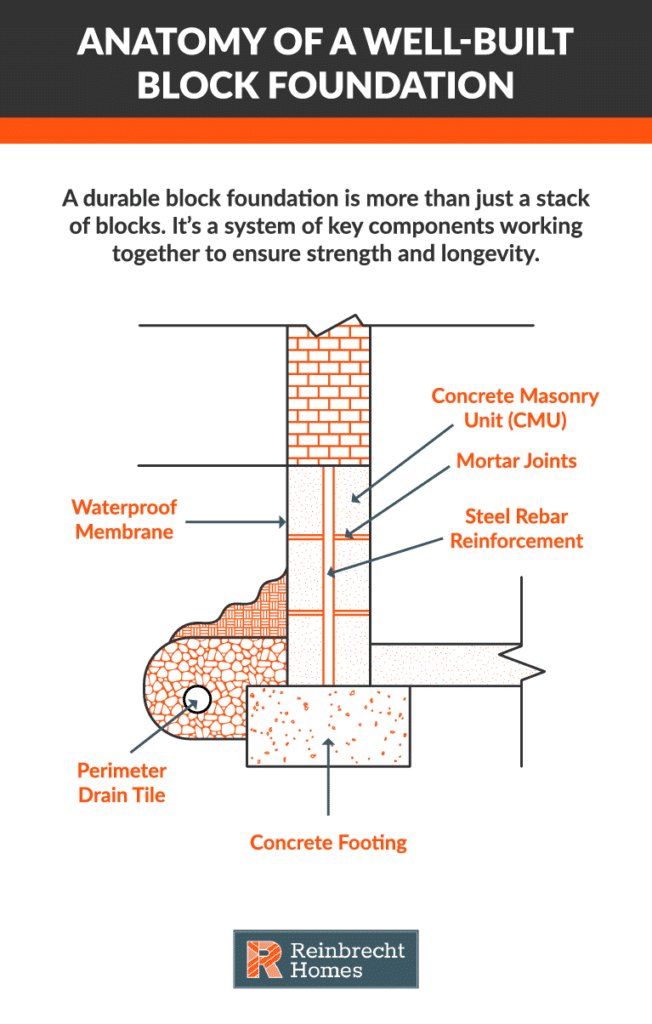
A block foundation is constructed from individual concrete masonry units (CMUs)—commonly known as concrete blocks—stacked systematically and bonded together with mortar to create the home’s structural base. While they are a popular and time-tested choice, their true value lies in a critical trade-off between materials, labor, and the non-negotiable need for proper reinforcement and water management.
Understanding this balance is key to making an informed decision. Here are the core considerations:
The Cost Equation: Materials vs. Labor
The most common perception is that block foundations are cost-effective. While the raw materials (the blocks themselves) are often less expensive than the large volume of concrete required for a poured wall, the installation is significantly more labor-intensive.
Each block must be laid and mortared by hand, a process that requires skill and time. Consequently, the final cost heavily depends on local labor rates and project complexity, and it may not always be the cheaper option once installation is factored in.
Strength and Stability: The Need for Reinforcement
Block foundations possess excellent compressive strength, making them highly effective at supporting the vertical weight of a home. However, their ability to resist lateral pressure from surrounding soil and water depends entirely on proper reinforcement. To prevent walls from bowing or cracking over time, steel rebar is installed vertically within the block cores and often horizontally within the mortar joints. This steel skeleton is what gives the foundation its tensile strength and long-term stability.
Durability and Water Management: A Critical Partnership
The primary vulnerability of a block foundation is its thousands of mortar joints. If left unprotected, these joints can provide pathways for water intrusion. Because of this, high-quality exterior waterproofing and a robust drainage system are not optional upgrades—they are essential components for long-term durability. A well-designed system will prevent water pressure from building against the walls, protecting both the structure and the interior (basement or crawl space) from moisture.
In short, when properly reinforced, waterproofed, and installed by skilled professionals, a block foundation is an incredibly durable and reliable choice that offers the unique advantage of being easier to repair than monolithic concrete.
How Block Foundations Compare to Alternatives
Unlike other common options like poured concrete or slab foundations, block foundations consist of individual units that can be replaced if needed. In contrast, poured concrete forms monolithic walls with fewer joints, which often improves water resistance and lateral strength.
While block foundations balance durability with modular repair advantages, they usually require extra measures—such as thorough waterproofing and additional reinforcement—for optimal performance in regions with high moisture or dynamic soil movement.
The Construction Process for Block Foundations
Building a block foundation involves several critical steps:
- Site Preparation and Grading: The process begins with proper site preparation. Clearing debris, leveling the ground, and grading the soil ensure that water is directed away from the foundation, reducing the risk of moisture intrusion.
- Laying the Footings and Stacking the Blocks: Footings are poured according to engineered plans to distribute loads evenly. Once the footings cure, concrete blocks are laid row by row with mortar between them. Steel reinforcements, such as rebar, are often inserted into the block cores to add strength and enhance both vertical and lateral stability.
- Waterproofing and Quality Assurance: After construction, a waterproof coating or membrane is applied to the foundation’s exterior. Perimeter drain tiles—or similarly effective drainage systems—help channel water away. Builders also verify that materials and workmanship adhere to high standards, ensuring proper alignment and installation. For more specific maintenance tips, see these foundation maintenance tips.
Common Issues and Proactive Maintenance
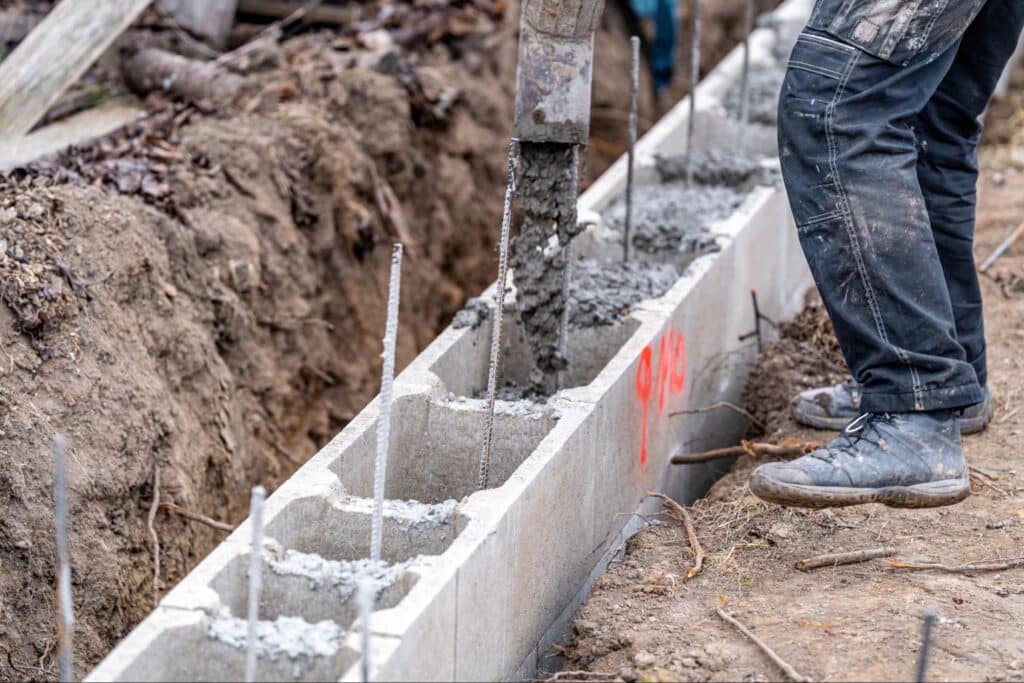

While durable, block foundations require proactive care to prevent common issues from developing. By understanding the potential challenges and their solutions, you can ensure your foundation remains stable and dry for its entire lifespan.
1. Challenge: Water Intrusion
Water is the primary adversary of a block foundation. It can seep through mortar joints or build up pressure against the walls, leading to leaks, moisture in your basement or crawlspace, and even structural damage over time.
Prevention & Maintenance:
- Ensure Proper Drainage: The most critical step is to manage water at the surface. Grade the soil so it slopes away from your home, and ensure gutters and downspouts are clean and extend at least four to six feet away from the foundation.
- Rely on Quality Waterproofing: During construction, a high-quality waterproof coating or membrane is applied to the exterior. This is your primary defense against subsurface water.
- Inspect and Seal: Regularly inspect the interior and exterior of your foundation for signs of dampness. Seal any small cracks or deteriorating mortar joints promptly to prevent minor issues from worsening.
2. Challenge: Cracking and Settling
Minor hairline cracks can appear as a home settles naturally. However, larger, horizontal, or stair-step cracks can indicate more significant structural stress from soil pressure or improper support.
Prevention & Maintenance:
Start with a Solid Base: Proper soil compaction and correctly sized footings during the construction phase are essential to minimize excessive settling.
- Trust in Reinforcement: Adequate steel reinforcement within the block cores is the key to resisting the forces that cause significant structural cracks.
- Monitor and Repair: Conduct regular visual inspections of your foundation walls. Small vertical cracks can often be sealed to prevent water entry, but if you notice cracks widening or expanding, it’s time for a professional evaluation.
3. Challenge: Bowing Walls
When excessive moisture saturates the soil outside, it expands and creates immense lateral (sideways) pressure on foundation walls. Over time, this can cause walls to lean or bow inward.
Prevention & Maintenance:
- Prioritize Water Management: The same steps used to prevent water intrusion—effective gutters, proper grading, and foundation drains—are your best defense against the soil pressure that causes bowing.
- Manage Landscaping: Keep large trees and shrubs with aggressive root systems a safe distance from your home, as their roots can exert pressure on foundation walls.
- Act Early: If you notice any inward movement or bulging in your foundation walls, contact a foundation specialist immediately. Early intervention can prevent a much more serious and expensive repair.
4. Challenge: Mortar Deterioration
The mortar that binds the blocks together can break down over decades of exposure to weather and moisture, creating gaps that weaken the wall and allow pests and water to enter.
Prevention & Maintenance:
- Seal Where Necessary: In areas with harsh weather exposure, applying a quality masonry sealant can help protect the mortar.
- Tuckpoint When Needed: If you see mortar crumbling or washing out, the solution is “tuckpointing”—a process where the old, damaged mortar is removed and replaced with fresh, durable mortar to restore the integrity and appearance of the joints.
Emerging Trends in Block Foundation Construction
Innovations in building practices continually refine block foundation construction. Builders are:
- Testing new additives in mortar to enhance resistance to freeze-thaw cycles.
- Integrating smart drainage systems that monitor moisture levels in real time.
- Incorporating green construction practices, such as recycled materials and eco-friendly sealants.
- Utilizing advanced surveying and modeling software for precise planning.
Adopting forward-thinking methods helps optimize both strength and energy efficiency, although effective moisture control and lateral stabilization remain key to long-lasting foundations.
The Reinbrecht Homes Approach to Block Foundations

With over 30 years of home building experience, Reinbrecht Homes emphasizes quality craftsmanship, durability, and clear communication. Their approach includes:
- Quality Craftsmanship: Using premium materials and meticulous construction methods to build homes that endure for decades, including careful attention to foundation work.
- Tailored Home Designs: Whether building on your own lot or in one of their neighborhood developments, Reinbrecht Homes adapts foundation designs to suit local soil and climate conditions. For those seeking semi-custom or fully custom options, block foundations offer the flexibility to be adapted to a wide range of floor plans, ensuring the home’s design remains both distinctive and structurally sound.
- Commitment to Longevity: Reinbrecht Homes prioritizes sturdy, well-reinforced, and properly waterproofed foundations to ensure that each home remains robust over time.
The Lasting Impact of Block Foundations in Home Construction
Block foundations, when designed and maintained correctly, provide a reliable and versatile base for homes. They deliver solid vertical support and notable durability, especially when reinforced, though their labor-intensive installation and vulnerability to moisture in certain climates require careful planning and maintenance. Whether your home is custom-built or semi-custom through Reinbrecht Homes, a well-constructed block foundation remains a crucial factor in ensuring that your investment stands the test of time. Ready to begin your homebuilding journey? Contact Reinbrecht Homes to find the perfect starting point for your new home.

