Building or purchasing a home near the Ohio River offers a unique lifestyle complete with scenic views and a close-knit community. However, this setting also presents challenges associated with floodplain and drainage. Whether you’re seeking a fully customized house or exploring semi-custom homes, understanding floodplain basics is crucial. This guide outlines core principles to mitigate flood risks and explains the importance of effective drainage systems. You’ll also learn how experienced builders, including the Reinbrecht Homes team, integrate these considerations to create safe, durable, and attractive homes in the region.
Why Understanding Floodplain and Drainage Basics Matters
Constructing or living near a major waterway requires proactive planning. Addressing floodplain and drainage considerations protects your safety and investment by:
- Ensuring Safety: Effective flood mitigation safeguards your family and belongings during extreme water events.
- Preserving Property Value: Flood-resistant features help maintain property values over time.
- Reducing Costs: Well-planned designs can lower insurance premiums and reduce repair expenses.
- Ensuring Compliance: Meeting local floodplain regulations helps avoid construction delays and penalties.
By prioritizing these factors early, you lay the groundwork for a home that is both structurally sound and compliant with safety standards.
Flood Zones and Their Impact on Home Building
Flood zones are geographical areas classified by their level of flood risk by agencies such as FEMA. Knowing your property’s flood zone is essential for planning and compliance.
Types of Flood Zones
Flood zones are typically designated as follows:
- Zone A or AE: Areas with a 1% annual chance of flooding, known as the 100-year floodplain.
- Zone VE: High-risk areas affected by both flooding and storm surge.
- Zone X (Shaded and Unshaded): Lower-risk areas, where shaded X indicates a 0.2% chance of flooding and unshaded X represents minimal risk.
These classifications dictate insurance requirements and construction standards. Even in lower-risk zones, incorporating proactive flood mitigation is advisable.
The Role of Flood Maps
FEMA flood maps provide key data such as:
- Base Flood Elevation (BFE): The expected water rise during a flood.
- Floodways: Channels where water flows most forcefully.
- High-Risk Zones: Areas that require extra building precautions.
Using these resources helps ensure your construction plans align with local ordinances and minimizes potential financial liabilities.
Financial Implications of Flood Zone Designations
Flood zone classifications influence insurance premiums and permitting fees. Homes built above the BFE using flood-resistant materials may benefit from lower insurance costs and reduced regulatory fees, making early planning a cost-effective decision.
Designing Homes to Mitigate Flooding Risks
Building in a flood-prone area requires thoughtful design that balances safety with aesthetic appeal.
Elevating Structures
Elevating a home above the base flood elevation is one of the most effective flood mitigation strategies. Raising living areas on stilts or an elevated foundation creates a protective buffer against rising water.
Using Flood-Resistant Materials
Incorporate materials that can withstand water exposure, such as:
- Concrete or Masonry Foundations: Designed to resist water penetration.
- Flood-resistant Insulation: Materials that maintain performance despite moisture.
- Waterproof Flooring: Options like sealed concrete or tile reduce damage after exposure.
These choices help maintain the structural integrity of your home during flooding events.
Incorporating Flood Vents
Flood vents allow water to flow through non-critical spaces like crawl spaces, reducing pressure against structural walls and lowering damage risk. Proper installation of these vents can also contribute to lower flood insurance premiums.
Custom Solutions for Specific Challenges
Flood risks can vary by location. Custom design solutions might include:
- Reinforced foundations for fast-moving floodwaters.
- Multi-use elevated spaces that combine storage with living areas.
- Tailored landscaping and retaining walls designed to manage site-specific water flow.
Such customizations ensure that each home is built with consideration for its unique environmental challenges without compromising on style.
Ensuring Effective Drainage Systems for Ohio River–Area Homes
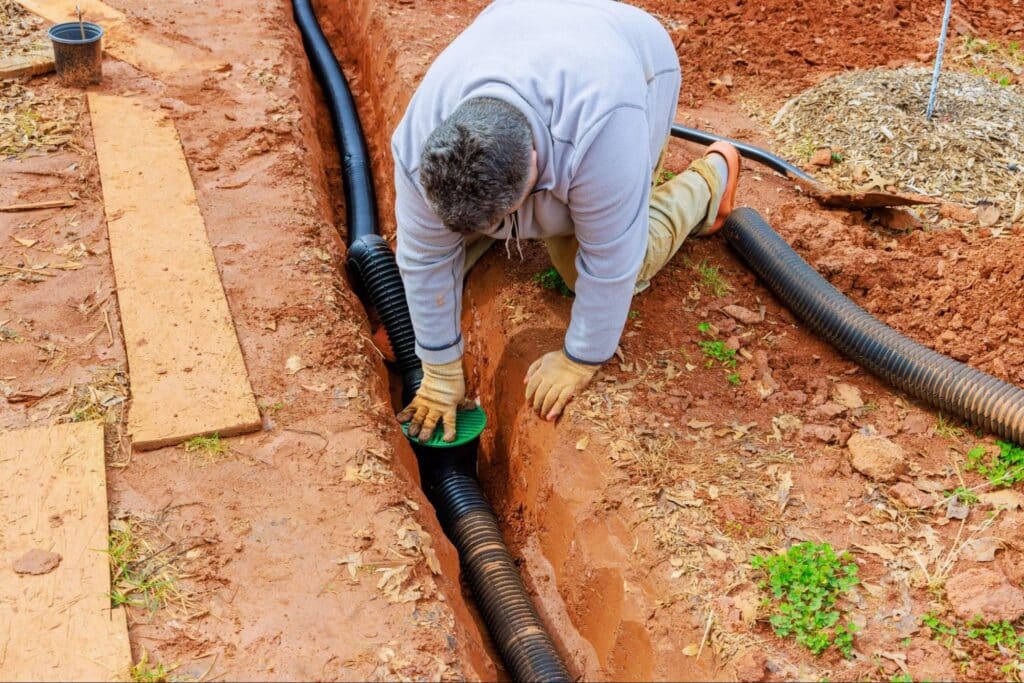

A reliable drainage system is essential to protect your home from water damage. Proper drainage prevents issues like foundation erosion, moisture buildup, and structural damage.
Key Drainage Components
Every effective drainage system incorporates:
- Grading and Sloping: Shaping the landscape so that water naturally flows away from the home.
- Gutters and Downspouts: Capturing roof runoff and directing it safely away.
- French Drains: Intercepting and redirecting groundwater.
- Sump Pumps: Actively removing accumulated water from basements or crawl spaces.
These elements work together to manage water and protect your property effectively.
Integrating Drainage with Landscaping
Strategic landscaping further supports drainage efforts. Techniques include:
- Swales and Berms: To channel water flow away from critical areas.
- Native Plants: That absorb moisture and stabilize soil.
- Permeable Paving: Allowing water to infiltrate rather than run off.
Combining these practices with mechanical systems creates a comprehensive solution that enhances property value while preventing water damage.
Practical Tips for Homebuyers and Builders Near the Ohio River
Consider these actionable tips to ensure your home is both beautiful and resilient:
- Select an Experienced Builder: Choose professionals with a proven record of addressing regional water and drainage challenges.
- Research Flood Zone Requirements: Use FEMA maps and local resources to understand your property’s risk level.
- Evaluate Site Conditions: Assess elevation, drainage, and soil stability before finalizing your purchase.
- Monitor Construction Progress: Use available tools to track progress and ensure flood mitigation measures are properly implemented.
- Obtain an Elevation Certificate: This document confirms your property’s base flood elevation, aiding in planning and insurance considerations.
Financial Considerations for Floodplain Construction
While building in a floodplain may involve higher upfront costs, these investments yield long-term benefits:
- Upfront Costs vs. Savings: Elevated foundations and drainage systems may increase initial expenses but often result in lower repair and insurance costs.
- Insurance Benefits: Homes built with flood mitigation measures typically qualify for reduced flood insurance premiums.
- Cost-Effective Compliance: Working with experienced builders can minimize unexpected permitting fees and regulatory delays.
- Flexible Financing: Builders often offer financing solutions, including construction loans, to ease the burden of additional costs.
- Long-Term Maintenance: Regular upkeep of drainage systems preserves home value and ongoing safety.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Understanding legal and regulatory issues is crucial when building near the Ohio River. Local, state, and federal regulations often govern floodplain construction and drainage requirements. Navigating these areas effectively requires attentive planning, familiarity with local ordinances, and accurate documentation.
Different counties throughout Southern Indiana and Eastern Illinois impose specific regulations for construction in elevated areas, especially near riverbanks. These requirements may outline minimum foundation heights, mandatory setbacks from floodways, or additional engineering approvals for drainage modifications. Reinbrecht Homes works in tandem with local zoning offices to ensure each project meets or exceeds these standards.
Moreover, state and federal guidelines—often derived from FEMA classifications—add another layer of requirements. Staying updated with these evolving standards is essential for maintaining compliance, preventing fines, and qualifying for preferable insurance rates. By verifying flood zone documentation, confirming BFE data, and conducting soil and land surveys, both builders and homeowners reduce long-term risks and ensure a smooth overall process.
Ongoing Maintenance and Preparedness
Constructing a flood-resilient home is only part of the equation—ongoing care is equally important. It’s crucial to perform regular inspections of gutters, sump pumps, and grading to maintain the protective measures installed during construction. Checking for blockages in downspouts, testing backup power systems for pumps, and evaluating soil settlement near your foundation help prevent small issues from escalating.
For properties near the Ohio River, periodic reviews of local levee systems and community drainage infrastructure can be beneficial. Maintaining open communication with neighbors and local officials fosters collaboration on broader floodplain management efforts, ensuring the area remains prepared for high-water events. Following a detailed maintenance schedule and staying informed helps preserve the long-term stability and safety of your flood-resistant home.
Emerging Trends in Flood-Resilient Home Design
The field of flood-resilient construction is continuously evolving. New research and technologies offer improved ways to mitigate flood damage and enhance overall home safety.
Advances in Materials and Construction Techniques
Recent innovations in flood-resistant technology include advanced waterproof materials, smart drainage systems, and energy-efficient design approaches that contribute to overall resilience. These breakthroughs are set to revolutionize how homes in flood-prone areas are built.
The Role of Smart Home Technology
Smart home solutions are becoming increasingly common in floodplain construction. Sensors can monitor water levels and humidity in real time, alerting homeowners when flood conditions arise. Moreover, integrated systems can automatically activate sump pumps or adjust window shutters to reduce water damage.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Sustainable building practices are increasingly vital in flood-prone environments. Incorporating green infrastructure—such as rain gardens and permeable paving—not only helps manage stormwater but also minimizes environmental impact. Building designs that emphasize sustainability often result in reduced utility bills and a lower ecological footprint, making them attractive to environmentally conscious buyers.
The Future of Floodplain Construction
As climate change leads to more unpredictable weather patterns, the need for resilient, adaptive construction methods becomes even more critical. Ongoing studies into the long-term effects of rising water levels and changing flood dynamics continue to inform best practices in home building. Future constructions will likely integrate more advanced monitoring tools, weather-resistant designs, and community-wide infrastructure planning to mitigate risk, help ensure every home is prepared for future challenges.
Reinbrecht Homes’ Expertise in Building Safe Ohio River Homes

With more than 30 years of experience in home building across Southern Indiana and Eastern Illinois, Reinbrecht Homes has developed a robust history in the region, which has given them an appreciation for local conditions. Their extensive experience translates into homes designed with attention to practical challenges such as water and drainage management.
Navigating Floodplain Regulations
Reinbrecht Homes is well-versed in local floodplain maps, FEMA standards, and zoning permits. This familiarity helps ensure that each project complies with safety standards while minimizing potential risks. They monitor local municipal and county policies for Southern Indiana and Eastern Illinois to provide up-to-date guidance on building codes and drainage requirements. By anticipating evolving regulations, they help clients save time, avoid penalties, and maintain clear communication with planning boards.
Proven Flood-Resistant Strategies
Key methods employed include:
- Elevating homes above the base flood elevation.
- Integrating flood vents to manage water pressure.
- Using waterproof and flood-resistant materials.
Whether constructing a fully customized house or opting for semi-custom homes, Reinbrecht Homes applies these methods to ensure durability and security. By tailoring each project to the client’s individual preferences, they focus on blending comfort, personalization, and robust flood-resilient design.
Transparent Project Oversight
Utilizing Buildertrend, Reinbrecht Homes provides clients with real-time updates throughout the building process. This transparency allows homeowners to understand how flood mitigation and drainage solutions are integrated into their home. By prioritizing local regulatory requirements and maintaining open lines of communication, they streamline the path from blueprint to finished property.
Frequently Asked Questions About Building in an Ohio River Floodplain
Do I need flood insurance if I build near the Ohio River in Indiana/Illinois?
If your home is in a high‑risk flood zone (A or AE) and you have a mortgage, your lender will almost always require flood insurance. In lower‑risk Zone X areas, it’s usually optional but still wise near the Ohio River.
Can I have a basement in a floodplain near the Ohio River?
Basements are often restricted or discouraged in high‑risk zones because they’re prone to flooding and costly damage. Some local codes near the Ohio River may prohibit basements below BFE, so always confirm with your county and builder.
How high should my home be built above the Base Flood Elevation?
Most communities require your lowest floor to be at least at BFE, and many along the Ohio River add 1–2 feet of freeboard above that. Your survey and design team will set the exact elevation based on FEMA maps and local rules.
Who provides an elevation certificate, and when do I need it?
A licensed land surveyor, engineer, or architect prepares your Elevation Certificate. You’ll typically need it for permitting and for your flood insurance once the home is built.
How long does permitting take for a floodplain home in Southern Indiana/Eastern Illinois?
Floodplain permits usually take longer than standard builds, often several weeks to a few months depending on the county and complexity. Using a builder familiar with local Ohio River regulations can help streamline approvals.
Building for a Secure Future along the Ohio River
Building or purchasing a home near the Ohio River presents both incredible opportunities and distinct challenges. By understanding floodplain fundamentals, implementing innovative design strategies—such as using an elevated foundation, installing flood vents, selecting flood-resistant materials, and ensuring a comprehensive drainage system—you can create a safe and resilient home built to last.
If you are ready to embark on your homebuilding journey near the Ohio River, schedule a consultation with Reinbrecht Homes today. Let our considerable local experience guide you toward building a home that offers security, longevity, and peace of mind for you and your family.

