Your home is more than just a building—it’s a major financial commitment and a repository for your cherished memories and possessions. Property insurance is essential to protect against unforeseen events that could lead to costly damages or losses. Whether you own a house or rent an apartment, understanding your insurance options is key to safeguarding both your property and your financial stability.
In recent years, scientists have noted that shifting weather patterns can increase the intensity of certain extreme events, including severe storms or heavy rainfall. Even if there is not always a clear long-term upward trend in the frequency of these occurrences, preparing for potential impacts through proper insurance coverage is especially important. By recognizing the variety of available policy types, you can make informed decisions that help protect your physical assets and your future security.
This guide breaks down different property insurance options, from standard coverage to specialized plans addressing risks like floods and earthquakes. It also provides real-life examples and actionable tips to help you select the most suitable policy. Read on to learn how to align your insurance choices with your unique needs and risk factors.
Homeowners Insurance: Comprehensive Protection for Property Owners
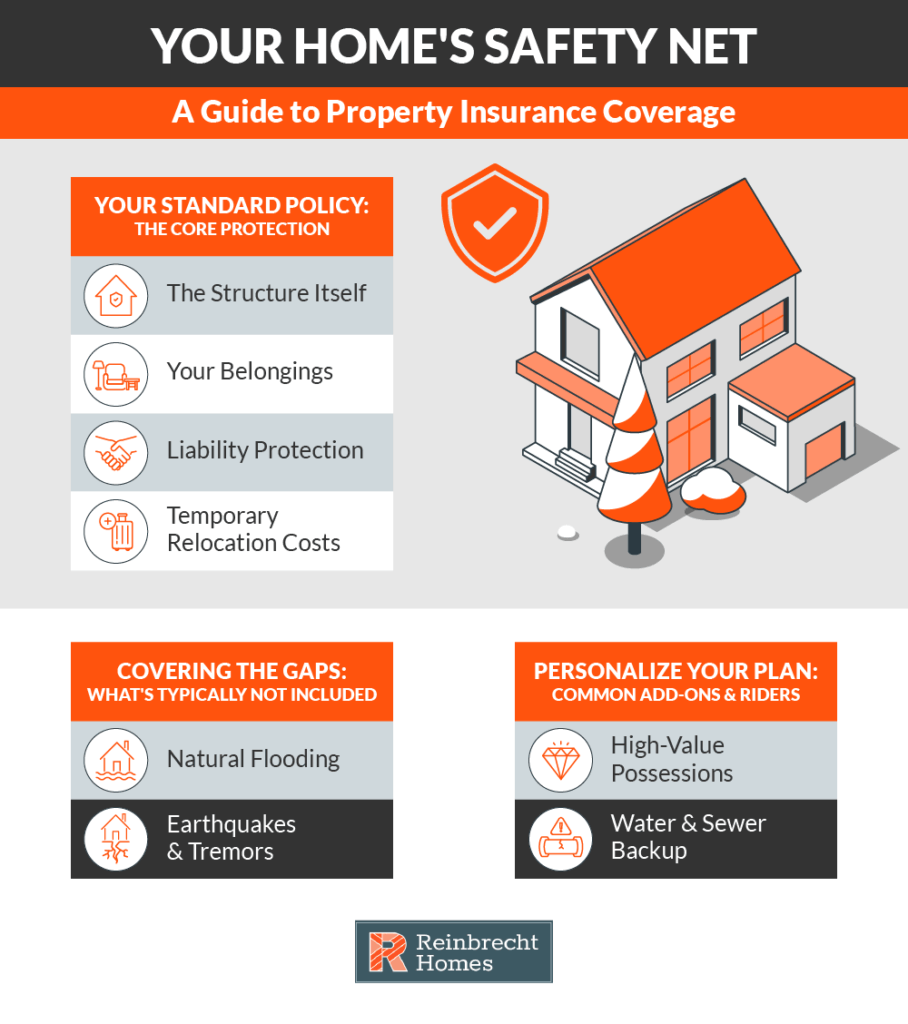
Homeowners insurance is often considered the foundational layer of property protection. It typically safeguards your home’s structure, your personal belongings, and provides liability coverage if accidents occur on your property. Purchasing a standard policy gives you peace of mind that many common risks—from fire damage to liability claims—are covered under one umbrella.
Key Components of Homeowners Insurance
A standard homeowners policy usually includes several crucial components:
- Dwelling Coverage: Pays for repairing or rebuilding your home if it’s damaged by covered perils, such as fire or wind.
- Other Structures Coverage: Protects standalone structures on your property, like a detached garage or tool shed.
- Personal Property Coverage: Insures your belongings—furniture, electronics, and clothing—based on either replacement cost or actual cash value.
- Liability Coverage: Covers legal fees and certain medical expenses if a visitor is injured on your property and sues.
- Additional Living Expenses (ALE): Pays for temporary housing and related costs if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered peril.
Policy Limitations and Riders
While homeowners insurance offers wide-ranging protection, standard policies often exclude losses stemming from floods or earthquakes. To address such gaps, many homeowners opt to add riders or endorsements for high-value items or for region-specific hazards. If you live in an area prone to flooding or seismic events, a rider or additional specialized coverage can prove invaluable.
Real-Life Examples
- House Fires: If a kitchen fire damages the home, homeowners insurance can help repair the structure, replace belongings, and cover the cost of temporary accommodation.
- Burglaries: When valuable items are stolen during a break-in, personal property coverage helps reimburse you for replacements.
- Injury Liability: If a guest trips on a loose step and sustains injuries requiring medical care, liability coverage can help pay for treatment and legal expenses.
Additional Considerations for Homeowners
Review your coverage annually—particularly if you have performed renovations or acquired expensive possessions. Many insurers offer premium discounts for installing safety features like robust security systems. While these measures cannot eliminate every weather-related risk, they may reduce the severity of potential damage and help limit claim costs.
Renters Insurance: Protection for Tenants
Renters insurance is designed for individuals who lease their homes but still need protection for personal belongings and personal liability. Landlords commonly maintain insurance on the building itself, yet tenants remain responsible for the contents of their own units and any liability arising from accidents they cause.
Essential Coverage for Renters
Key elements of a renters insurance policy typically include:
- Personal Property Protection: Secures your belongings—like electronics, clothing, and furniture—against dangers such as theft, fire, or water damage. Flood coverage frequently requires an additional or separate policy.
- Liability Coverage: Helps cover the costs of property damage or accidental injuries for which you are legally accountable. For instance, if a fire starts in your unit and spreads to a neighboring apartment, you can be held financially responsible.
- Additional Living Expenses (ALE): Contributes toward interim lodging and expenses if a covered event, such as a fire, renders your rental uninhabitable.
Benefits and Practical Scenarios
- Apartment Theft: Renters insurance covers stolen items, lessening your out-of-pocket replacement costs.
- Accidental Damages: If you accidentally damage the rental property—such as staining the carpet—liability coverage can manage associated repair expenses.
- Displacement Costs: In the event that a covered peril requires you to find temporary housing, ALE coverage helps cover additional living costs until your rental is habitable again.
Enhancing Renters Insurance Value
Special or high-cost items (jewelry, collectibles, and so forth) might exceed standard coverage limits. Consider riders to provide sufficient protection. Also, some insurers offer discounts when you bundle renters insurance with other policies. As your circumstances evolve, updating your policy ensures you remain protected.
Addressing Gaps: Specialized Insurance and Riders
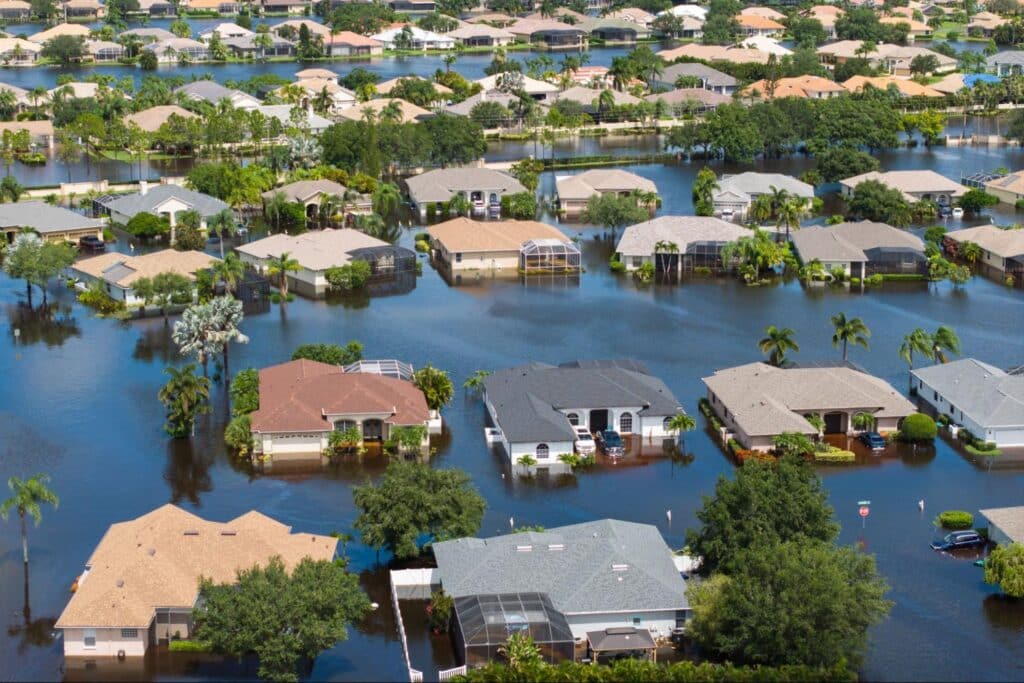

While homeowners and renters policies are comprehensive, they don’t cover everything. Standard policies often exclude catastrophic events like floods and earthquakes, and may have limits on high-value items. Specialized insurance and riders exist to fill these critical gaps.
Flood Insurance: Protection Against Water Damage
Because many homeowners and renters policies exclude flood damage, purchasing separate flood insurance is necessary for at-risk properties. This is especially true for regions with frequent downpours or proximity to coastal areas. Flood insurance typically includes building property coverage (for the structure) and personal contents coverage (for belongings). Research local floodplains to understand your exposure. Many people obtain coverage through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), though private insurers also offer policies.
Earthquake Insurance: Safeguarding Against Seismic Events
Similarly, most standard policies exclude losses from earthquakes. Dedicated earthquake insurance is crucial if you live near an active fault line. Policies typically cover damage to your home’s structure (dwelling coverage), your household items (personal property), and temporary lodging (ALE). Even moderate quakes can cause costly structural damage, making this coverage essential in seismic zones.
Optional Riders for Customized Protection
You can further tailor your policy with endorsements, or riders, to cover unique risks:
- High-Value Item Riders: Provide extra coverage for items like fine jewelry, art, or collectibles that exceed the basic policy limit.
- Water Backup and Sump Overflow Riders: Expand coverage to events such as sewer or sump pump failure—situations that most standard policies exclude.
How Home Construction and Trends Impact Your Insurance

Beyond choosing the right policy, the physical characteristics of your home and emerging environmental trends play a significant role in your long-term security and insurance costs. Proactive planning, especially during the homebuilding process, can lead to substantial savings and better protection.
The Future of Insurance and Home Resilience
The property insurance landscape is adapting to changing environmental conditions. Insurers are using advanced data analytics to predict threats and refine premiums. Staying informed about these trends helps you adjust your coverage proactively.
At the same time, advancements in construction can make homes more resilient. Technological innovations and eco-friendly building methods influence your insurance needs. Many modern homes feature advanced materials that withstand elements more effectively than older structures.
Integrating Insurance Planning into Your Homebuilding Process
When buying or building a home, considering property insurance early on is highly valuable.
- Resilient Design: During the planning stages, explore how your home’s design may affect premiums. Using wind-resistant materials, reinforced roofing, or installing robust drainage systems can lessen storm-related damage risks and potentially lower insurance costs.
- Energy-Efficient Upgrades: Features like solar panels, modern insulation, or storm shutters may qualify you for policy discounts.
- Quality Construction: Builders with a proven track record of quality often collaborate with clients to design a house that not only meets aesthetic preferences but also reduces potential claims.
By taking a proactive approach, you can align crucial home features with insurance savings. For many homeowners, especially those building semi-custom or fully custom properties, this holistic strategy translates to lower overall costs and better peace of mind.
Practical Tips for Purchasing the Right Property Insurance Policy
Selecting the best insurance involves identifying your personal risk factors, balancing coverage with premiums, and staying adaptable to changes in your circumstances.
1. Evaluate Your Coverage Needs
Create an itemized list of your home, belongings, and risk exposures, then decide which events—like floods or earthquakes—warrant extra coverage. This comprehensive assessment prevents potential gaps.
2. Compare Policy Features and Costs
Obtain quotes from multiple providers. Look beyond the premium to focus on coverage limits, deductibles, and exclusions, ensuring you pay only for what you need while securing essential protection.
3. Understand Policy Exclusions
Even robust plans frequently omit floods, earthquakes, and certain other perils. Recognize these exclusions and arrange separate or supplementary coverage if your environment or lifestyle requires it.
4. Seek Expert Guidance
Insurance terms and conditions can be complicated. Seasoned professionals can provide clarity regarding deductibles, riders, or endorsements you might need based on your geographic and personal profile.
5. Periodically Review and Update Your Policy
Assess your policy whenever you complete home improvements or acquire expensive items. Keeping coverage up to date helps ensure your financial security evolves alongside life changes.
6. Consider Bundling Policies
Many insurers offer discounts for bundling policies, such as combining home and auto insurance. Not only can this lead to cost savings, it also consolidates policy management into one convenient package.
Making Informed Decisions and Future-Proofing Your Property
Property insurance is a fundamental safeguard against risks that might otherwise disrupt your life, finances, and sense of security. Deciding among comprehensive homeowners insurance, targeted renters coverage, or specialized policies for flood or earthquake damage requires a clear understanding of your home, possessions, and local conditions.
While reviewing your policies, consider supplemental riders or endorsements to address any uncovered exposures. Keep current with policy trends and new construction techniques that can minimize damage from severe weather and other perils. By integrating thoughtful insurance planning—particularly if you are building or upgrading a home—you create a more resilient living space that aligns with your personal and financial goals.
If you’re exploring a new build or want guidance on safeguarding your dream home, we invite you to learn more about coverage options as part of your overall planning. Contact Reinbrecht Homes today for help assessing your property insurance needs and discovering how our construction approach in Southern Indiana and Eastern Illinois can offer added peace of mind.

